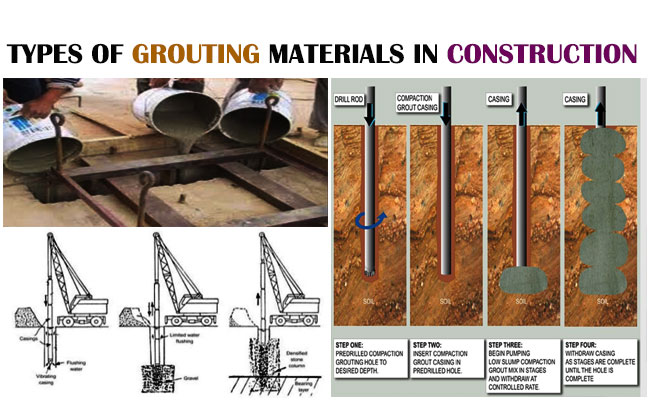
Types of grouting materials in construction

Grout refers to any viscous (solid and sticky liquid that never flows simply), packable material that is applied to fill the space among two elements for binding them or to produce a water-resistant seal.Grout is normally a mixture of cement, sand and water to fill spaces. They are suitable for repairing of concrete cracks, fill seams and spaces in tiles, seal and fill spaces for waterproofing, and for maintain stability of soil. It is also effective for providing additional strength to the foundations of load-bearing structures.
Grouting Materials
Various types of materials are found for grouting:
Cement Grouting:
Cement (or cementitious grout) is a common type of grouting materials having a greater penetrability. The ratio of neat cement and water or a mixture of sand (4 parts) to cement (1 part) is used for cement grouting.
Holes are created in a radius across the excavating area prior to inject with a thin grout, then the water cement ratio is decreased to raise the viscosity of grout. When necessary, secondary holes are created among the primary holes to enable the complete grouting of the area.
Bentonite Grouting:
Bentonite is formed with clay that contains thixotropic properties. It can develop a highly water-proof gel that can be blended with additives to produce a permanent barricade to water flow. It is suitable where soil particles are very tiny for cement grouting, normally to check leakage in alluvial soils underneath the foundations of dams or other water-bound structures.
Chemical Grouting:
Chemical grouting is suitable for the soils of medium to coarse grading. Materials like sodium silicate and calcium chloride are blended jointly in liquid form and hardened into a gel with the following methods :-
‘Two-shot’ process: Pipes are pushed into the ground. One chemical is injected accompanied by another implying that the reaction, and soil strengthening, is fast.
‘One-shot’ process: It entails chemical mixing before injection, with the hardening being deferred by the composition. It facilitates larger borehole spacing.
Chemical grouting can arrange reasonable spacing of bore holes, higher infiltration of the grout, and more flexibility regarding the time of grouting.
Resin Grouting:
Resin grouts contain a very low viscosity to infiltrate fine sands. The type of resin is utilized on the basis of the chemical content of the local water table and may lead to different times for setting.
The following types are generally found:
- Tannin-based grouts.
- Phenol-formaldehyde.
- Resorcinol formaldehyde.
Bituminous Grouting:
Bitumen emulsion acts as a useful grouting material to be injected into fine sands as an impervious obstacle to water. Soil strength is not raised, but cut-off walls under dams and other water-bound structures are produced efficiently.
Definition of Construction Grout:
Grouting means the injection of pumped materials into a soil or rock construction to modify its physical properties. Grout may also be used in the formation of pile foundations, ground anchors, under reaming, underpinning, in road construction, dam construction, and so on.
Based on the soil or rock type, the area where grouting will be used and other factors, several materials are utilized for grouting. But the fundamental method is similar by injecting the fluid grout to the soil or rock that sets and shrinks or functions as a sealant on the material’s penetrability.
The common types of grouting materials are cement grouting, bentonite grouting, chemical grouting, resin grouting, bituminous grouting.